
Our data will be in a single data frame (with no labels, just fields). The most well known graphic depicting part-to-whole relationships is the pie chart. It might also contain a string field represening the region name. We frequently run into questions that are best answered by visualizations of part-to-whole relationships: total revenue by country or product, total incidents by turbine, genome read variants by chromosome, &c. It can also contain an (optional) additional string field for grouping the different series.įor the above example, our data will contain a time field, a number field that represents the number of requests, and a string field representing the server name. From the second example, you see the White color products are the least selling in all the countries. The R Mosaic Plot draws a rectangle, and its height represents the proportional value. The vertical length of the bars is proportional to the number of observations in the second variable within each level of the first variable.

For two variables, the width of the columns is proportional to the number of observations in each level of the variable plotted on the horizontal axis. The data frame must contain a time field, a numeric Amplitude field and a string Breakdown field to differentiate the different series. The Mosaic Plot in R Programming is very useful to visualize the data from the contingency table or two-way frequency table. A mosaic plot is a special type of stacked bar chart. This data format is applicable when all of the data is in a single data frame. When using the heatmap data format, each row is mapped to a specific data frame For example, each frame might look something like this: Time The data will be presented in multiple frames, where each frame corresponds to a specific combination of label values. The mosaic plot, also known as a mosaic diagram, is a graphic method for the visualization of data sets with two or more qualitative variables (characteristics). It might also contain a string label represening the region name. It is the multidimensional extension of spineplots, which graphically display the same information for only one variable. It can also contain an (optional) additional string label for grouping the different series.įor example, let's assume that we want to plot the number of requests hitting a number of different serversįor the above example, our data will contain a time field, a number field that represents the number of requests, and a string label representing the server name. A mosaic plot, Marimekko chart, or sometimes percent stacked bar plot is a graphical visualization of data from two or more qualitative variables. This data format is applicable where each data frame has a time field, a numeric Amplitude field and a string Breakdown label to differentiate the different series. It’s also called crosstabs or two-way table and it’s used to summarize the relationship among several categorical variables.
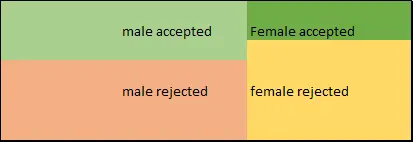
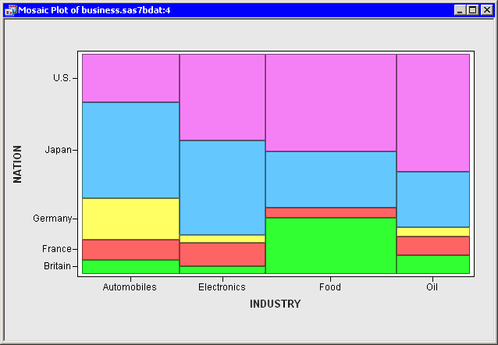
To get the numbers behind the previous plot, a contingency table is needed. A collection of rectangles represents all the elements to be visualized with the rectangles of different sizes and colors makes a table, but what makes these mosaic charts unique is the arrangement of the elements where there is a hierarchy those elements are collected and labeled together, perhaps even with subcategories. The mosaic plot is based on conditional probabilities. It was previously referred to as the `Regular Data Format` Mosaic plots are a great way to visualize hierarchical data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
